Observability and Tracing for the Vercel AI SDK
This notebook demonstrates how to integrate Langfuse with the Vercel AI SDK to monitor, debug, and evaluate your LLM-powered applications and AI agents.
What is the Vercel AI SDK?: The Vercel AI SDK is a lightweight toolkit that lets developers call and stream responses from AI models (like OpenAI, Anthropic, or any compliant provider) directly in web apps with simple server/client functions.
What is Langfuse?: Langfuse is an open-source observability platform for AI agents and LLM applications. It helps you visualize and monitor LLM calls, tool usage, cost, latency, and more.
1. Install Dependencies
Install the Vercel AI SDK, OpenTelemetry, and Langfuse:
npm install ai
npm install @ai-sdk/openai
npm install @langfuse/tracing @langfuse/otel @opentelemetry/sdk-node2. Configure Environment & API Keys
Set up your Langfuse and OpenAI credentials. You can get Langfuse keys by signing up for a free Langfuse Cloud account or by self-hosting Langfuse.
LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY = "sk-lf-..."
LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY = "pk-lf-..."
LANGFUSE_BASE_URL = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
# LANGFUSE_BASE_URL = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region
OPENAI_API_KEY = "sk-proj-"3. Initialize Langfuse
The Langfuse TypeScript SDK’s tracing is built on top of OpenTelemetry, so you need to set up the OpenTelemetry SDK. The LangfuseSpanProcessor is the key component that sends traces to Langfuse.
import { NodeSDK } from "@opentelemetry/sdk-node";
import { LangfuseSpanProcessor } from "@langfuse/otel";
const sdk = new NodeSDK({
spanProcessors: [new LangfuseSpanProcessor()],
});
sdk.start();4: Instrument your application
The Vercel AI SDK offers native instrumentation with OpenTelemetry. You can enable the Vercel AI SDK telemetry by passing { experimental_telemetry: { isEnabled: true }} to your AI SDK function calls.
import { generateText } from "ai";
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
const { text } = await generateText({
model: openai("gpt-5"),
prompt: "What is Langfuse?",
experimental_telemetry: { isEnabled: true },
});Another example using tools.
import { generateText, tool } from 'ai';
import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
import { z } from 'zod';
const { text } = await generateText({
model: openai("gpt-5"),
prompt: 'What is the weather like today in San Francisco?',
tools: {
getWeather: tool({
description: 'Get the weather in a location',
inputSchema: z.object({
location: z.string().describe('The location to get the weather for'),
}),
execute: async ({ location }) => ({
location,
temperature: 72 + Math.floor(Math.random() * 21) - 10,
}),
}),
},
experimental_telemetry: { isEnabled: true },
});5. See traces in Langfuse.
After running the workflow, you can view the complete trace in Langfuse:
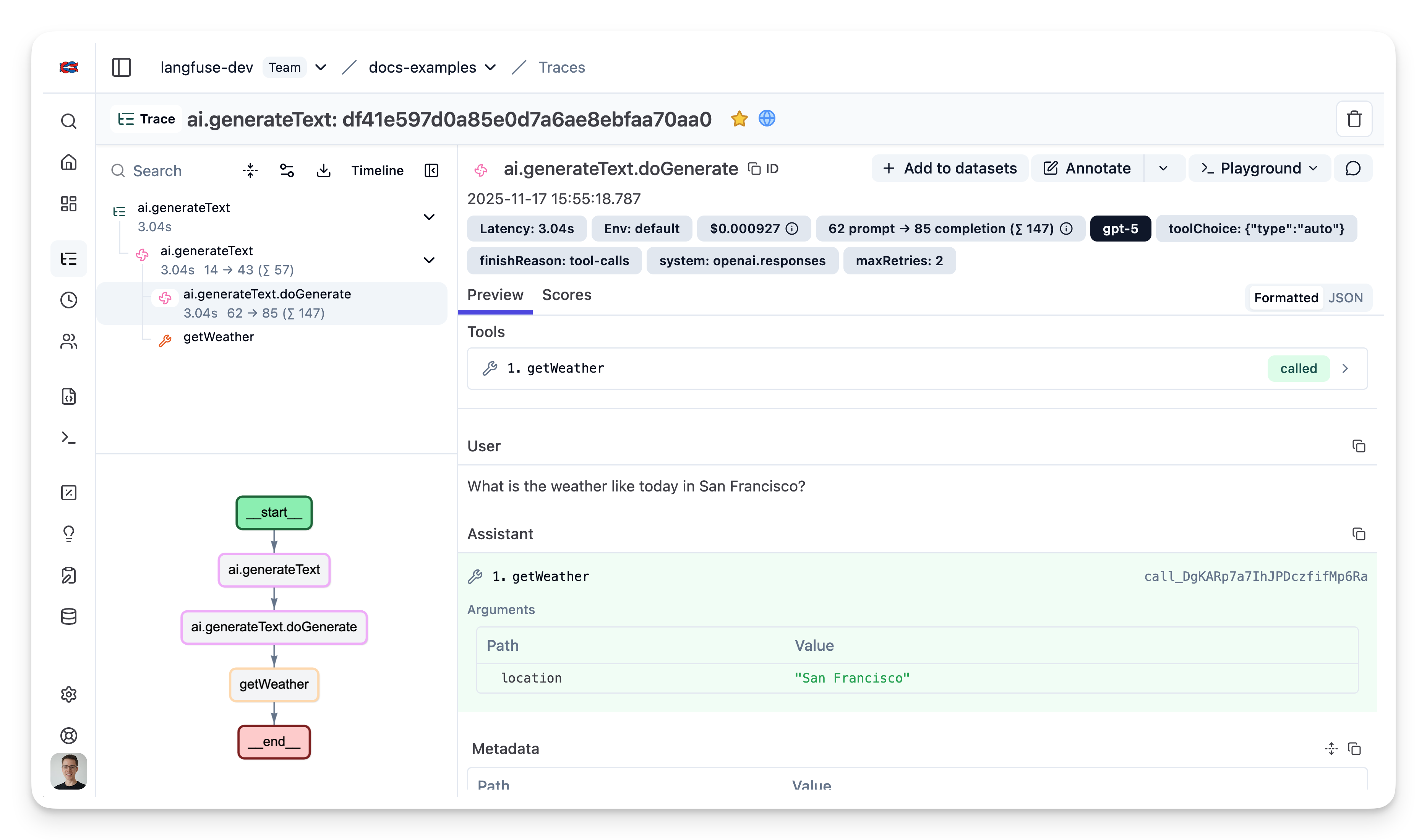
Example Trace: View in Langfuse
Learn more about the AI SDK Telemetry in the Vercel AI SDK documentation on Telemetry.
Next.js Example
Here is a full example on how to set up tracing with the
- AI SDK v5
- Next.js
- Deployed on Vercel
Create a new file instrumentation.ts in your project root with the following content:
// instrumentation.ts
import { LangfuseSpanProcessor, ShouldExportSpan } from "@langfuse/otel";
import { NodeTracerProvider } from "@opentelemetry/sdk-trace-node";
// Optional: filter our NextJS infra spans
const shouldExportSpan: ShouldExportSpan = (span) => {
return span.otelSpan.instrumentationScope.name !== "next.js";
};
export const langfuseSpanProcessor = new LangfuseSpanProcessor({
shouldExportSpan,
});
const tracerProvider = new NodeTracerProvider({
spanProcessors: [langfuseSpanProcessor],
});
tracerProvider.register();If you are using Next.js, please use a manual OpenTelemetry setup via the
NodeTracerProvider rather than via registerOTel from @vercel/otel. This
is because the @vercel/otel package does not yet support the OpenTelemetry
JS SDK v2 on which the
@langfuse/tracing and @langfuse/otel packages are based.
// route.ts
import { streamText } from "ai";
import { after } from "next/server";
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
import {
observe,
updateActiveObservation,
updateActiveTrace,
} from "@langfuse/tracing";
import { trace } from "@opentelemetry/api";
import { langfuseSpanProcessor } from "@/src/instrumentation";
const handler = async (req: Request) => {
const {
messages,
chatId,
userId,
}: { messages: UIMessage[]; chatId: string; userId: string } =
await req.json();
// Set session id and user id on active trace
const inputText = messages[messages.length - 1].parts.find(
(part) => part.type === "text"
)?.text;
updateActiveObservation({
input: inputText,
});
updateActiveTrace({
name: "my-ai-sdk-trace",
sessionId: chatId,
userId,
input: inputText,
});
const result = streamText({
// ... other streamText options ...
experimental_telemetry: {
isEnabled: true,
},
onFinish: async (result) => {
updateActiveObservation({
output: result.content,
});
updateActiveTrace({
output: result.content,
});
// End span manually after stream has finished
trace.getActiveSpan().end();
},
onError: async (error) => {
updateActiveObservation({
output: error,
level: "ERROR"
});
updateActiveTrace({
output: error,
});
// End span manually after stream has finished
trace.getActiveSpan()?.end();
},
});
// Important in serverless environments: schedule flush after request is finished
after(async () => await langfuseSpanProcessor.forceFlush());
return result.toUIMessageStreamResponse();
};
export const POST = observe(handler, {
name: "handle-chat-message",
endOnExit: false, // end observation _after_ stream has finished
});Using Prompt Management
You can use Langfuse Prompt Management to manage and fetch prompts from Langfguse and link LLM generations to prompt versions so you can understand how your prompts are performing and run experiments.
The key changes are:
- Import the Langfuse client
- Fetch your prompt using
langfuse.prompt.get() - Add the prompt to the observation metadata
- Pass
langfusePrompt: prompt.toJSON()in the telemetry metadata
import { generateText } from "ai";
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
import { LangfuseClient } from "@langfuse/client"; // Add this import
const langfuse = new LangfuseClient();
// Get current `production` version
const prompt = await langfuse.prompt.get("movie-critic");
// Insert variables into prompt template
const compiledPrompt = prompt.compile({
someVariable: "example-variable",
});
const { text } = await generateText({
model: openai("gpt-5"),
prompt: compiledPrompt,
experimental_telemetry: {
isEnabled: true,
metadata: {
langfusePrompt: prompt.toJSON() // This links the Generation to your prompt in Langfuse
},
},
});Interoperability with the JS/TS SDK
You can use this integration together with the Langfuse JS/TS SDK to add additional attributes or group observations into a single trace.
The Context Manager allows you to wrap your instrumented code using context managers (with with statements), which allows you to add additional attributes to the trace. Any observation created inside the callback will automatically be nested under the active observation, and the observation will be ended when the callback finishes.
import { startActiveObservation, propagateAttributes } from "npm:@langfuse/tracing";
await startActiveObservation("context-manager", async (span) => {
span.update({
input: { query: "What is the capital of France?" },
});
// Propagate userId to all child observations
await propagateAttributes(
{
userId: "user-123",
sessionId: "session-123",
metadata: {
source: "api",
region: "us-east-1",
},
tags: ["api", "user"],
version: "1.0.0",
},
async () => {
// YOUR CODE HERE
const { text } = await generateText({
model: openai("gpt-5"),
prompt: "What is the capital of France?",
experimental_telemetry: { isEnabled: true },
});
}
);
span.update({ output: "Paris" });
});Learn more about using the Context Manager in the JS/TS SDK docs.
Next Steps
Once you have instrumented your code, you can manage, evaluate and debug your application: